
The ocean is deep, dark, and full of mysteries. However, few creatures spark as much wonder as the giant squid. With eyes as big as dinner plates and arms that stretch like living ropes, this animal feels like it swam straight out of a legend. The biology of giant squid. helps us understand that this creature is not a monster, but a master of survival.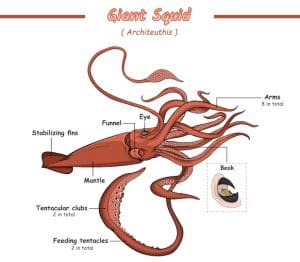
In this article, we will explore how it lives, how it hunts, how it grows, and why it matters. Moreover, we will explain everything in a clear and simple way, so even a child can imagine this giant drifting through the sea.
Contents
- What Is a Giant Squid?🐟
- The Body Structure: Built for the Deep🐟
- The Nervous System: Smart and Alert🐟
- Feeding and Hunting: A Silent Strategy🐟
- Reproduction: The Circle of Life🐟
- Growth and Lifespan: Fast and Short🐟
- Defense Mechanisms: Facing Giants🐟
- Habitat: Life in the Twilight Zone🐟
- Why The biology of giant squid. Matters🐟
- Fun Facts to Spark Curiosity🐟
- From Myth to Science🐟
What Is a Giant Squid?🐟
First of all, the giant squid is a marine animal that belongs to the cephalopod family. This group also includes octopuses and cuttlefish. Unlike fish, squid do not have bones. Instead, they have soft bodies that move with grace.
In fact, the scientific name of the giant squid is Architeuthis dux. Although that name sounds complex, its meaning is simple: “ruling squid.” And indeed, it rules the deep sea.
Key Characteristics
- Length: Up to 43 feet (13 meters)
- Weight: Around 600 pounds (275 kg)
- Habitat: Deep ocean waters
- Diet: Fish and other squid
- Predators: Mainly sperm whales
Therefore, when we talk about The biology of giant squid., we are exploring the body systems, behavior, and survival skills of one of the largest invertebrates on Earth.
The Body Structure: Built for the Deep🐟
Now, let’s dive deeper into its body. The giant squid has three main parts: the mantle, the head, and the arms.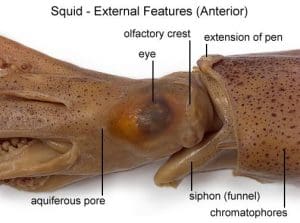
The Mantle: The Power Center
The mantle is the long, tube-shaped body. It holds most of the squid’s organs. For example, the heart, gills, and digestive system are inside it.
Moreover, the mantle helps the squid move. It pulls water in and then pushes it out quickly. As a result, the squid shoots backward through the water. This movement is called jet propulsion.
The Arms and Tentacles: Tools for Survival
Unlike octopuses, giant squid have eight arms and two longer tentacles. The tentacles grab prey, while the arms hold it tight.
Each arm has suckers lined with tiny, sharp edges. Therefore, when the squid catches something, it rarely escapes.
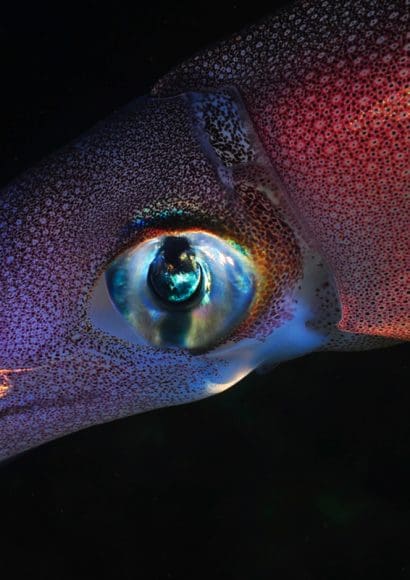
The Eyes: Giants of the Animal Kingdom
Perhaps the most amazing feature is its eyes. Giant squid have the largest eyes of any animal on Earth. Each eye can be about 10 inches (25 cm) wide.
Because the deep ocean is dark, large eyes help detect even small amounts of light. As a result, the squid can see predators and prey from far away.
The Nervous System: Smart and Alert🐟
Although it lives in darkness, the giant squid is not slow or dull. On the contrary, it has a complex nervous system.
Its brain forms a ring around its esophagus. While that sounds strange, it works very well. The squid can react quickly to danger. For instance, if a sperm whale approaches, the squid may try to escape with a burst of speed.
Furthermore, like other cephalopods, giant squid likely have strong problem-solving skills. Scientists continue to study this area, and new discoveries appear each year.
Feeding and Hunting: A Silent Strategy🐟
Now let’s talk about food. Giant squid are carnivores. That means they eat meat.
How They Hunt
First, they float quietly in the water. Then, when prey swims close, they shoot out their long tentacles. In seconds, the prey is trapped.
After that, the squid uses its beak to bite. The beak looks like a parrot’s beak, but it is much stronger. It tears food into small pieces.
Because food is rare in the deep sea, the squid cannot waste energy. Therefore, it waits patiently instead of chasing prey for long distances.
Reproduction: The Circle of Life🐟
Reproduction in giant squid remains partly mysterious. However, scientists have learned some important facts.
Male squid transfer sperm to females using a special arm. Afterward, females release thousands or even millions of eggs into the water.
Unlike mammals, giant squid do not care for their young. Once the eggs hatch, the baby squid must survive on their own. As a result, only a small number reach adulthood.
Nevertheless, this strategy works. By producing many eggs, the species continues.
Growth and Lifespan: Fast and Short🐟
Interestingly, giant squid grow very fast. In fact, they may reach full size in just a few years.
However, their lifespan is short. Most scientists believe they live around 3 to 5 years.
This fast growth rate helps explain their huge size. They eat often, grow quickly, and reproduce before they die. In other words, their life moves at high speed.
Defense Mechanisms: Facing Giants🐟
Of course, life in the deep sea is not easy. The sperm whale is the giant squid’s main predator.
When attacked, the squid may fight back. Scars found on sperm whales show that squid use their arms and suckers to defend themselves.
Additionally, squid can release a cloud of ink. This dark cloud confuses predators and allows escape.
Therefore, even though it is hunted, the giant squid is far from helpless. To understand the immense power of the ocean, read The most devastating tsunamis on record: stories of waves that changed the world.
Habitat: Life in the Twilight Zone🐟
Giant squid live in deep ocean waters, usually between 1,000 and 3,000 feet below the surface.
This zone is cold and dark. Sunlight barely reaches it. Because of this, the squid’s body is adapted for low light and high pressure.
Moreover, scientists rarely see live giant squid in their natural habitat. Most knowledge comes from stranded individuals or deep-sea cameras.
As technology improves, however, more secrets are revealed.
Why The biology of giant squid. Matters🐟
You may wonder why studying this creature is important. After all, it lives far from us.
However, understanding The biology of giant squid. helps scientists learn about deep-sea ecosystems. The deep ocean covers most of our planet. Therefore, when we study its creatures, we learn about Earth itself.
Furthermore, giant squid play a role in the food chain. They control fish populations and serve as prey for whales. If they disappeared, the balance of the deep sea would change.
In addition, their unique biology inspires technology. For example, their jet propulsion system influences underwater vehicle design.
Thus, this giant is not just a myth. It is a key player in ocean life.
Fun Facts to Spark Curiosity🐟
To make things even more exciting, here are some surprising facts:
- Giant squid blood is blue.
- They have three hearts.
- Their beak is the only hard part of their body.
- Battles between squid and whales leave scars that tell stories.
- They were once believed to be sea monsters called “kraken.”
Clearly, truth can be just as thrilling as fiction. If you’re curious about the health benefits hidden in marine life, explore our guide on Omega-3 fatty acids in seafood: A simple and friendly guide for everyone.
From Myth to Science🐟
For centuries, sailors told stories about massive sea monsters. However, today we know that these legends likely came from real encounters with giant squid.
Thanks to science, mystery turns into knowledge. And yet, wonder remains.
The biology of giant squid. shows us how life adapts, survives, and thrives in extreme places. It teaches us that even in darkness, nature finds a way.
So next time you look at the ocean, remember: deep below the waves, a gentle giant drifts through the silent blue.

